Page 67 - PSPS: A Training guide
P. 67
Adequate nutrition and physical activity will support the young child’s physical
development and their ability to effectively partake in school activities. Physical activity
and movement are also a key element of a child’s mental health. It can form an
essential element of the transitions process, providing bonding opportunities, fun, and
offering a change from the time spent sitting in the classroom.
On average, children spend almost half of their day in the school environment so it is
important that all opportunities to encourage and promote physical activity during that
time are utilised.
During the transition process there is an opportunity to foster good habits around
movement, activity and healthy eating that will endure throughout the child’s lifetime.
These habits of movement are general, not specifically linked to sports programmes,
and are part of a long-term healthy lifestyle. Sports programmes will play a role for
some children; however, the broader patterns of regular movement can be developed
through good practice in the early years of school, especially beginning during the
transitions phase. Afterall, we know that active children are far more likely to grow to
become active adults.
Addressing those Needs
The early classroom years provide a golden opportunity for helping children’s physical
development. They are at the optimum age for building good movement skills and
physical literacy, which equates with verbal, linguistic and mathematical literacy,
supporting all aspects of learning.
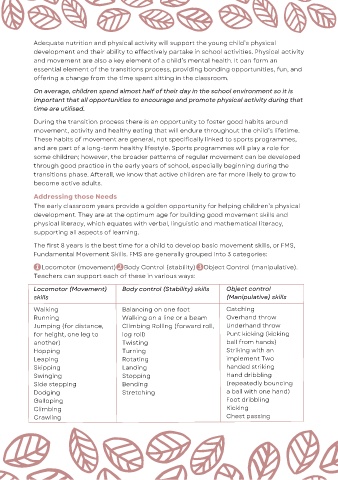
The first 8 years is the best time for a child to develop basic movement skills, or FMS,
Fundamental Movement Skills. FMS are generally grouped into 3 categories:
Locomotor (movement) Body Control (stability) Object Control (manipulative).
Teachers can support each of these in various ways:
Locomotor (Movement) Body control (Stability) skills Object control
skills (Manipulative) skills
Walking Balancing on one foot Catching
Running Walking on a line or a beam Overhand throw
Jumping (for distance, Climbing Rolling (forward roll, Underhand throw
for height, one leg to log roll) Punt kicking (kicking
another) Twisting ball from hands)
Hopping Turning Striking with an
Leaping Rotating implement Two
Skipping Landing handed striking
Swinging Stopping Hand dribbling
Side stepping Bending (repeatedly bouncing
Dodging Stretching a ball with one hand)
Galloping Foot dribbling
Climbing Kicking
Crawling Chest passing